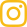
Split Leather
They are rough on both outer surfaces due to the separation of the grain carrying layer. The area facing the splitting knife is in most cases considered as the surface and will be treated accordingly so that we also have to distinguish in this case between:
finished split leather,
coated split leather and
suede split leather
The area of split leathers is reduced to the core parts so that double-butts result as the preferred kind for marketing bovine splits. The undersides of the splits are checked during the sorting regarding any remaining subcutaneous vein web or subcutaneous tissue in order to distinguish the texturally firmer flesh splits or lower splits from the middle splits.
Finished Split Leather
Split leathers need to get an altogether thicker finish layer in order to get a surface comparable to finished full-grains as the rough split surface has to be covered. It can also be treated with various emboss pattern, like dressed full-grains. The cross-section will show, after cutting these split leathers that the finish sits on the compact fibers of the reticular layer, i.e. that in contrast to finished full-grains the grain layer or to corrected leathers the fine fibers of the upper papillary layer are missing. The rough split leather surface will be visible after removing the finish with relevant solvents.
Coated Split Leather
Coated split leathers are laminated with a foil in contrast to the top coats that are built-up through step-by-step layers. The expression “coated” has only to be used if the applied layer is thicker than 0.15mm. The thickness ratio between leather and foil will furthermore decide whether it can still be called leather or not.
Suede Split Leather
Suede split leathers are mostly buffed on the upper split side so that also in this case a check of the flesh-side is possible which will indicate if a flesh- or middle-split is present. Middle splits are used as a stiffening material or for reinforcements as the sole use is often not sufficient due to the fastness of this leather. These splits show on both sides equally rough surfaces from the inner reticular layer so that subcutaneous veins are missing as do the remnants of the subcutaneous tissue. Middle splits are also finished but only in very special cases (interior partitions of briefcases).